The Mini Complete Guide to the Science of Sleep and How We Can Improve Our Sleep Using Technology
- Saygin Celen
- Oct 24, 2023
- 6 min read
We theoretically spend 1/3rd of our lives asleep for a healthy and fulfilling wakeful lifetime. However, often, most people know very little about why we sleep and they don’t learn about how they can improve their sleep quality and time.

35% of the US population is sleep-deprived according to the Good Body. The global stats is 62% according to Healthmatch.
The lack of sleep and not learning how to improve it affect the quality of lives of billions of people.
In this story, I will dive into:
The Concise Science Behind Sleep and What Happens in Our Brains During Sleep
How We Can Improve Our Sleep Using Simple Methods
Top Technology and Practical Innovative Products to Improve Your Sleep without Using Any Medication
Let’s get started.
The Concise Science Behind Sleep
The Cleaning Process and Melatonin: A Nightly Ritual
While you rest peacefully during the night, your brain is actively engaged in an essential process known as the glymphatic system, responsible for cleaning and maintaining the brain’s health.

Source: Dr. JockersAt the same time, melatonin, the “sleep hormone,” plays a significant role in regulating this nightly brain-cleaning ritual.
The Glymphatic System and Brain Cleansing
The glymphatic system is a recently discovered waste clearance system that operates within the brain.
Much like the lymphatic system, which flushes waste from the body’s tissues, the glymphatic system removes toxins and other byproducts from brain cells.
How the Glymphatic System Works
During sleep, the cells in your brain shrink, creating more space between them.
This expansion allows cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to flow more efficiently through the brain tissue, flushing away waste products such as beta-amyloid, which is associated with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
This process resembles a nightly brain “shower.”
Melatonin’s Role
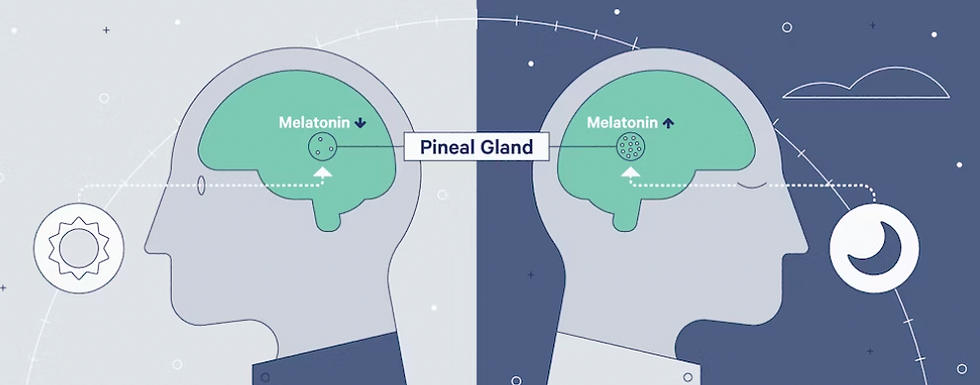
Melatonin, often referred to as the “hormone of darkness,” is produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It is intricately linked to your sleep-wake cycle and helps regulate the various stages of sleep.
Circadian Rhythm. Source: Casper Mattress
Melatonin production: Melatonin production is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light. As the evening progresses and the environment becomes dimmer, your pineal gland releases melatonin into the bloodstream. The resulting increase in melatonin levels signals to your body that it’s time to prepare for sleep.
Melatonin and the glymphatic system: Researchers have found that melatonin may enhance the glymphatic system’s activity. As melatonin levels rise during the night, this may contribute to the more efficient clearance of waste products in the brain. In essence, melatonin ensures that the brain’s “cleaning crew” is hard at work while you sleep.
Restorative sleep: The peak production of melatonin during the night is associated with deep, restorative sleep, particularly during the NREM stages. This is when the glymphatic system is most active, ensuring that waste products are effectively removed.
In summary, the glymphatic system and melatonin share a unique and interconnected relationship.
While you’re tucked in for the night, melatonin rises, signaling the brain’s cleaning process to begin.
This intricate balance of hormones and brain functions underscores the importance of obtaining a restful night’s sleep, not only for cognitive function but also for the long-term health of your brain.
So, the next time you drift off into dreamland, remember that your brain is engaged in its nightly cleaning ritual, thanks in part to the sleep-inducing properties of melatonin.
A Short Introduction to Other Sleep-Related Hormones
Melatonin isn’t the only sleep hormone. There are other hormones that create the balance and value of how and why we sleep.
The Full List of Sleep Hormones and What They Do
Cortisol Often referred to as the “stress hormone,” cortisol follows a diurnal rhythm, peaking in the morning to help you wake up and stay alert during the day.
It gradually decreases as the day progresses and reaches its lowest point during the night. This decline in cortisol is essential for initiating and maintaining restful sleep.
Adenosine Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that accumulates in the brain while you’re awake and gradually promotes drowsiness.
Caffeine, a common stimulant, works by blocking adenosine receptors, making you feel more awake. As you sleep, adenosine levels decrease, contributing to feeling refreshed upon waking.
Serotonin Known as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, serotonin is involved in mood regulation and also helps control the sleep-wake cycle.
Higher serotonin levels are associated with better sleep quality, as serotonin converts to melatonin during the night, aiding in the initiation and maintenance of sleep.
Ghrelin Ghrelin is a hunger-related hormone that may affect sleep by increasing the likelihood of nighttime snacking. Irregular eating patterns and late-night meals can impact sleep quality and disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle.
Leptin Leptin, on the other hand, is responsible for regulating satiety and energy balance. Poor sleep can lead to changes in leptin levels, contributing to an increased appetite, particularly for high-calorie foods.

Source: Niklas GustafsonGrowth Hormone (GH) Secreted primarily during deep sleep (slow-wave sleep or NREM sleep), GH is crucial for physical growth, muscle repair, and overall restoration. Sleep disturbances can negatively affect GH secretion.
Cytokines These proteins are involved in immune responses and are also linked to sleep. While you sleep, your body increases the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, supporting recovery from daily activities and maintaining overall health.
Dopamine Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in wakefulness, alertness, and mood regulation. Imbalances in dopamine levels can lead to sleep disorders or conditions like restless leg syndrome.
How We Can Improve Our Sleep Using Simple Methods
Healthy Sleep Habits and Lifestyle Changes

The Basics of Sleep Hygiene and Routines. Source: Very Well Mind
Building a Sleep-Conducive Environment
One of the keys to better sleep is creating a suitable sleep environment.
Creating a completely dark environment maximizes the sleep environment. Blackout curtains or eye masks can help do just that.
Here are great options for technology-enhanced Bluetooth Sleep Headphones:
Keeping the room temperature cooler than the ideal room temperature of 23 C or 72 F is also ideal for sleep conditions. A 20 C or 67 F room is seen as the ideal room temperature for sleep.
Also, air humidifiers and oil diffusers are amazing products for general health, and running them in your bedroom is a plus.
Here is a great air humidifier option:
The Role of Diet and Exercise
Diet and exercise can significantly impact the quality of your sleep.
Not eating 3 hours before certainly makes a big difference. Otherwise, eating right before you sleep makes your digestion system work while you sleep, which in a way ruins your sleep cycle and your energy recovery system.
Ideally, walking every day 10,000 steps and exercising 3–4 times a week actively also add much value to your sleep routine.
Stress Management for Better Sleep
Stress and anxiety can keep you up at night. Stress stimulates cortisol levels, which energizes the body, rather artificially and unnecessarily, keeping you up when you are supposed to rest.
Meditation is a great practice that calms the mind.
You can use such apps as Calm for meditation practices:
You can also learn more about meditation using amazing YouTube channels such as: Yongey Mingyur Rinpoche.

or a Buddhism channel or self-mastery channel such as: Shi Heng Yi
Sleep Hygiene: Creating Bedtime Rituals
Establishing a bedtime routine can signal to your body that it’s time to sleep. A daily bedtime routine is a set time to discipline and calm yourself half an hour to 1 hour before bedtime.
The bedtime routine consists of the things you do every day before sleep such as turning off screens, dimming the lights, meditating and reading a book.
Decide on a set bedtime.
Then, realize your bedtime routine 30 to 60 minutes before you go to bed.
Turn off all your screens. Blue light floods your brain and this suppresses melatonin production and keeps you awake.
Take a warm bath.
Drink a small cup of tea.
Meditate for at least 5 minutes. Relax your mind. Breath in and out deeply.
Stretch, breath, relax.
Read a book you like. Then, you can dream about the book.
Listen to relaxing music.
Prepare your bedroom. Set the room temperature to 20–22 C or 67–70 F. Dim the lights. Close the blackout curtains. Turn on your air humidifier /oil diffuser.
Top Technology and Practical Innovative Products
Improve Your Sleep without Using Any Medication
Snoring Chin Strap for Snoring Relief and Restful Sleep. Adjustable Mouth Guard Achieve peaceful sleep with Bokeds Anti-Snoring Chin Strap & Mouth Guard. End snoring troubles effortlessly.
Noise Reducing Ear Plugs for Sound Sleep and Quiet Nights
Unwind with Silicone Earplug Noise Reducing Ear Plugs. Embrace peaceful tranquility with these versatile noise-reducing earplugs.
Handheld Sleep Anxiety Therapy and Insomnia Help: The Ultimate Sleep Aid Device
Reclaim restful sleep with the Handheld Sleep Aid Device. Drug-free, portable, and tailored for serene nights.
ELAIMEI Sleep Strips for Snoring Relief and Peaceful Nights
Sleep soundly with ELAIMEI Anti Snoring Sleep Strips: Say goodbye to snoring and mouth dryness.
Travel Comfort Redefined: Inflatable Airplane Sleeping Pillow and Seat Cushion
Experience superior comfort on your journeys with the Upgraded Inflatable Sleeping Pillow: Ideal for travel by air, car, or office naps.
Wireless Sleep Headphones — Cozy Comfort for Sweet Dreams
Upgrade your sleep experience with Tiandirenhe Wireless Sleep Headphones Headband: Comfort meets audio enjoyment for an uninterrupted night’s rest.
KINSCOTER Aroma Diffuser & Air Humidifier with Night Light and Beautiful Design
Elevate well-being with the KINSCOTER Portable Mini Aroma Diffuser and Air Humidifier: Enhance your health and relaxation at home.


Comments